We Once Studied the World as if it was Flat...
Imagine what we’re missing by studying tissue in 2D
Discover what 2D spatial misses
Cellular relationships are the essence of spatial biology. The promise of the field lies in our ability to resolve:
- cellular heterogeneity
- cellular organization
- cell-cell interactions
- single cell omics
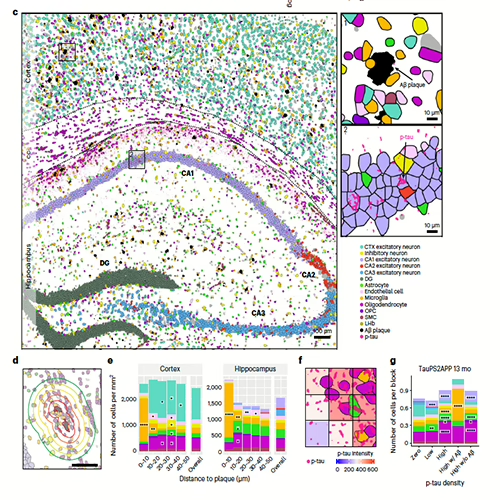
Yet, current industry-leading spatial technologies only glean insights from neighboring cells on a two-dimensional plane. Hover over the heatmap on the right to see the striking difference in the story told by 2D versus 3D tissue.
To see publication click here
Novel applications of 3D spatial biology
When it comes to tracking infrequent changes or impacts in a local area, 2D spatial analysis falls short. With 3D spatial biology powered by the Pyxa platform, you can survey a larger volume of cells within the same spatial area, increasing the odds of capturing a rare event, such as gene edits, formation of neural connections, cellular differentiation, or immune cell activation.
- Therapeutic Delivery
- CRISPR Screening In-situ
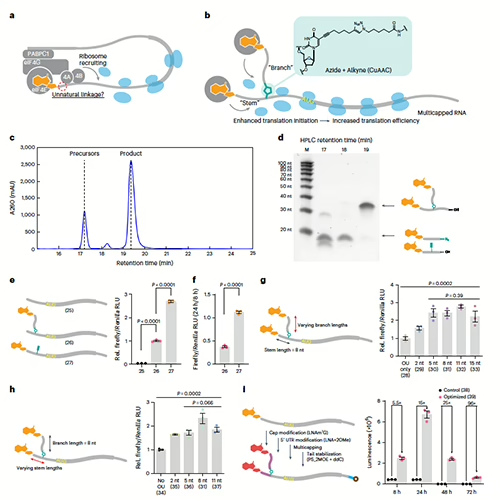
- Molecular Barcoding
- Cell morphology
- Organoid Screens
- Connectomics
3D uncovers more biology
The Pyxa platform adds another dimension of data
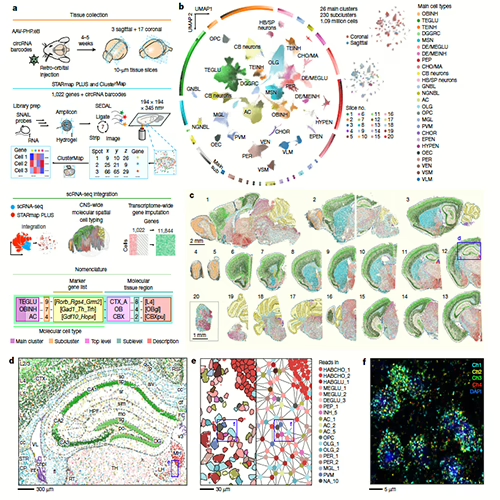
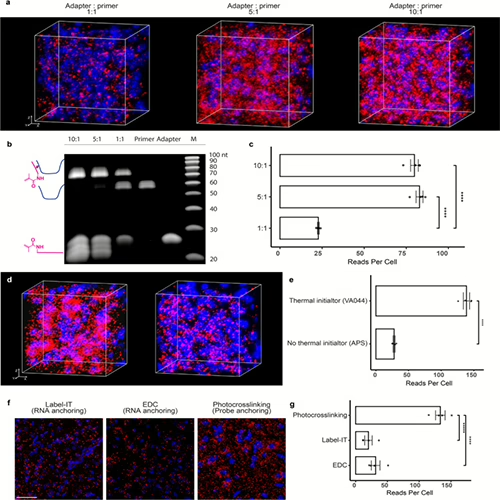
Pyxa incorporates STARmap technology for true spatial analysis of thick tissue slices.
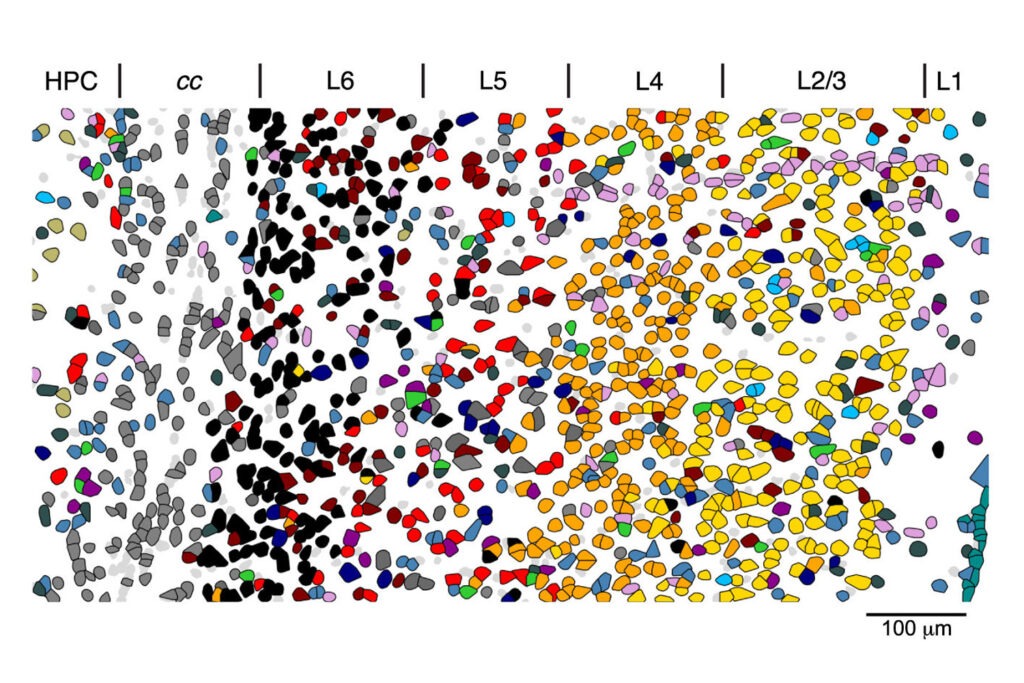
Expanding horizons for multiple therapeutic areas
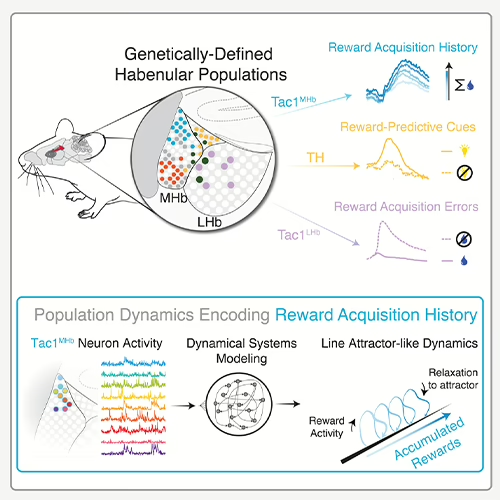
Neuroscience
- Brain atlas and cellular mapping across 3D neural networks.
- Correlation of CNS cells' gene expression patterns with their function and location.
- Precise neuronal network connectomics, including rare cell-to-cell connections often missed in 2D tissues.
Oncology
- Detect rare cell-to-cell communication events in immunotherapy drug resistance.
- Explore the spatial relationship between TILs and tumor cells and confirm TIL efficacy.
- Study tumor evolution in specific tumor types and organs with 3D resolution.
Advanced modalities
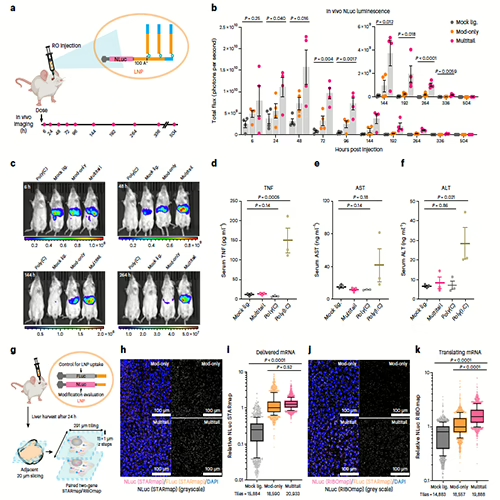
- Tracking CRISPR and CAR-T efficacy in-vivo, including rare edit events that 2D technologies miss.
- Identifying off-target changes, and measuring the radius to which edits extend.
- Measure local impact of payload on gene expression, T-cell activation, and translation for vaccine and protein therapy production.